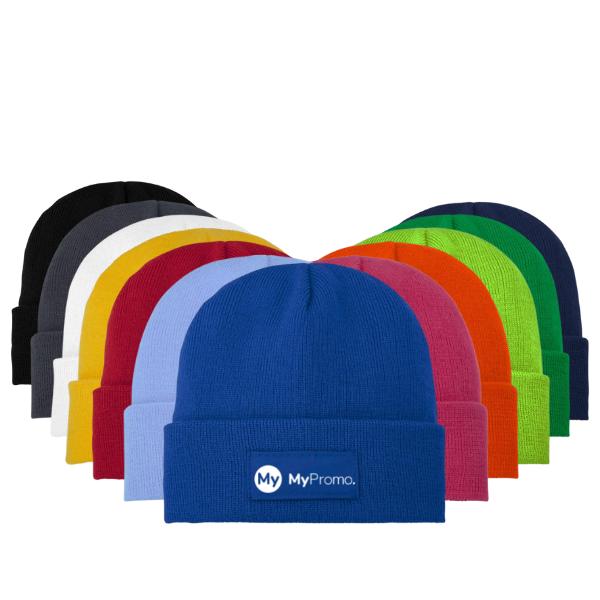
Embroidery fixed
What is embroidery fixed?
Embroidery fixed refers to a modern enhancement of traditional embroidery techniques that involves decorating fabric with machine-stitched designs using computerized technology. Originating in ancient China, Egypt, and Europe, embroidery was historically done by hand with luxurious threads like silk and gold. Today, it's achieved through digitized designs fed into embroidery machines, which precisely stitch patterns onto fabrics. This method adds personal and durable touches to corporate apparel, promotional items, and gifts, while maintaining a unique raised texture and intricate detailing that distinguishes it from other printing techniques.
Essential tools and materials for enhanced embroidery
To achieve high-quality results in modern embroidery, several key tools and materials are necessary:
- Embroidery Machines: Advanced machinery that can handle complex designs.
- Digitizing Software: Converts graphics into stitchable embroidery files.
- Threads: Variety in material (polyester, rayon, cotton) and color for different effects.
- Needles: Specific types designed for embroidery.
- Stabilizers: Support materials that hold fabric in place during the stitching process.
- Hoop or Frame: Keeps the fabric stretched and stationary.
Applications and notable examples
Embroidery fixed is commonly applied in personalizing corporate apparel, such as company uniforms, hats, and jackets, which helps in reinforcing brand identity. It's also popular in promotional gifting, like embroidered personalized towels or personalised bags, and decorative patches on various apparel. Notable for its use in high-end fashion, this technique adds a luxury element to everyday items.
Advantages of embroidery in printing techniques
The advantages of using modern embroidery in printing and personalization include:
- Durability: Embroidered designs are robust and can withstand heavy washing and wear without fading.
- Texture and Aesthetics: Offers a unique raised texture that can make a visual and tactile impact.
- Versatility: Suitable for almost any type of fabric and a wide array of products.
Comparing embroidery to other printing techniques
Unlike screen printing, which lays ink on top of the fabric, embroidery involves stitching that integrates the design into the material itself, offering a three-dimensional appearance and enhanced durability. Compared to digital printing techniques, embroidery provides not only a richer texture but also a more prestigious look.
Challenges and limitations
Despite its many benefits, embroidery fixed can come with challenges such as higher costs compared to simpler printing methods and limitations in design complexity and resolution. Thicker fabrics are typically required to support the weight of the stitching, which can limit application options. Additionally, the setup for embroidery can be time-consuming, influencing the overall production time.
What is embroidery fixed used for?
Embroidery fixed is commonly used to personalise corporate clothing like uniforms, jackets, and hats to reinforce brand identity. It's also popular for customised gifts, such as embroidered towels and bags, as well as decorative patches on various garments.
What tools and materials are essential for embroidery fixed?
Essential tools and materials include embroidery machines, digitising software, various threads (polyester, rayon, cotton), needles designed for embroidery, fabric stabilisers, and an embroidery frame or hoop.
How does embroidery fixed compare to screen printing?
Unlike screen printing, which applies ink on top of fabric, embroidery fixed incorporates the pattern directly into the material by sewing, giving a three-dimensional appearance and improved durability.
What are the main advantages of embroidery fixed over other techniques?
Embroidery fixed offers exceptional durability, raised texture with a tactile and visual impact, and versatility across different fabric types, providing a prestigious look.
What challenges might one face when using embroidery fixed?
Challenges include higher costs compared to simpler printing methods, limitations in design complexity, and the need for thicker fabrics to support embroidery weight. Additionally, the setup time for embroidery can impact overall production time.