Pad print
What is Pad print?
Pad print is a unique printing technique widely used to apply designs onto irregularly shaped or uneven surfaces. This method involves transferring ink from a silicone pad to various objects, allowing for intricate and detailed printing on surfaces like promotional gifts, electronic devices, or even automotive parts. Its versatility has made it a favorite in the printing industry for decades. Originating in the Swiss watch industry during the 1940s, pad print was initially used to print the intricate details on watch faces. The technique has since evolved to cover a broader range of applications. The process starts with creating an etched plate or cliché that holds the design. Ink is applied to the plate, and a silicone pad presses onto it to pick up the ink. The pad is then pressed onto the object to transfer the design, resulting in a high-quality, durable print. This simple yet effective technique allows pad print to remain a crucial part of the printing and promotional gifts industry.Essential Tools and Materials for Pad Print
Pad print relies on a specific set of tools and materials to achieve its distinct results. At the heart of the process is the silicone pad, which is designed to be flexible enough to contour to a wide variety of shapes while picking up and releasing ink effectively. The pad is paired with a cliché or etched plate containing the design to be printed. This plate is crucial as it defines the pattern that will be transferred onto the object. To complete the setup, a precision ink cup and pad-printing machine are required to control the application of ink and ensure accurate positioning during the transfer process.Ink is another critical component, with pad print inks designed to work on different substrates, including plastics, metals, glass, ceramics, and fabrics. These inks are typically quick-drying to ensure the printed design is durable and resistant to smudging or fading.
Applications of Pad Print in Promotional Products
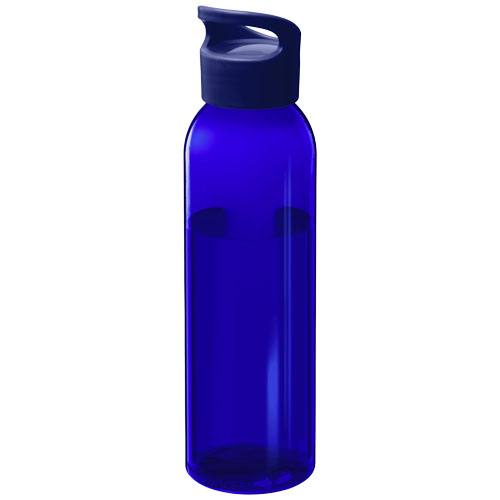
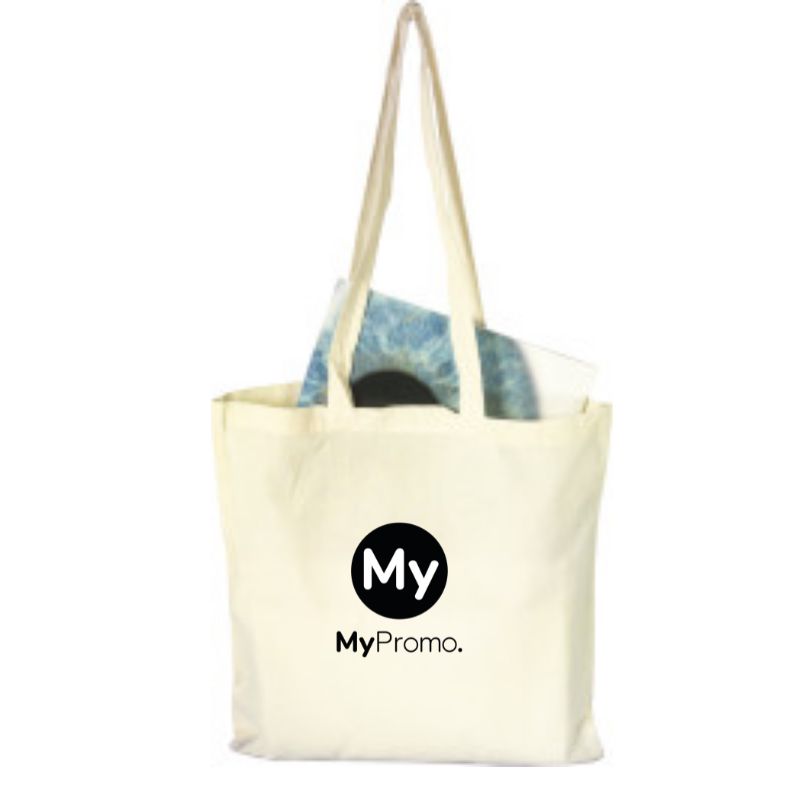
Pad print is a popular choice for personalizing promotional products due to its versatility. It can be used to print logos, text, or intricate designs on various items. Common examples include personalized pens, keychains, personalized mugs, personalized USB sticks, and stress balls. The technique's ability to print on curved or uneven surfaces makes it ideal for products with unique shapes. Businesses often choose pad print for promotional gifts because it can produce high-quality results on a wide range of materials, allowing them to create custom-branded items that are both functional and visually appealing.Advantages of Pad Print
One of the primary advantages of pad print is its adaptability. It can handle complex shapes and intricate details with relative ease, making it ideal for products with complex contours. The technique also allows for multi-color printing, enabling detailed and vibrant designs. Additionally, pad print is cost-effective for both small and large production runs, making it a flexible choice for businesses of all sizes. The inks used in pad print are generally durable, ensuring that the printed designs remain intact even with regular use or exposure to the elements.Comparing Pad Print with Other Techniques
Compared to other print techniques, pad print stands out for its ability to print on non-flat surfaces. While screen printing and offset printing excel on flat surfaces, pad print is better suited for items with curves or textures. However, pad print may not be as fast as digital printing for large-scale production, and the setup process can be more complex due to the need to create clichés for each design.Challenges and Limitations of Pad Print
Despite its many benefits, pad print has some limitations. The setup process can be time-consuming, as it requires creating a new cliché for each design change. This can increase costs for smaller production runs. The technique also has limitations in terms of print size; it may not be suitable for very large designs or wide-format printing. Additionally, while pad print allows for multi-color designs, the process of aligning multiple colors can be intricate and requires precision. Despite these challenges, pad print remains a versatile and valuable technique in the printing industry.This table would allow readers to quickly see how pad print compares with other printing techniques in terms of key factors like versatility, cost, and speed.
| Feature | Pad Print | Screen Printing | Offset Printing | Digital Printing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suitable for Curved Surfaces | Yes | Limited | No | Limited |
| Detailed and Multi-Color | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ideal for Small Runs | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Ideal for Large Runs | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate | Moderate | High | Low |
| Relative Cost | Moderate | Low | High | Moderate |
What is pad print?
Pad printing is a printing technique where a silicone pad is used to transfer ink from a plate to a substrate. It is commonly used for printing on irregular or curved surfaces, such as promotional items, electronic components, and medical devices.
How does pad print work?
Pad printing involves creating a plate with an etched design. Ink is applied to the plate, filling the etched areas. A silicone pad presses onto the inked plate, picking up the design, then transfers it onto the desired substrate. This process allows for precise and high-resolution printing.
What materials can be pad printed?
Pad printing can be applied to a wide variety of materials, including plastics, glass, metals, ceramics, textiles, and rubber. It is often used for printing on products with complex shapes and surfaces that are difficult to print with other techniques.
What are the advantages of pad print?
Pad printing offers several advantages, including the ability to print on irregular surfaces, high resolution and detail, versatility with various materials, and a relatively low setup cost compared to other printing methods. It is also adaptable to small and large production runs.
What are the common applications of pad printing?
Pad printing is commonly used in industries such as electronics, automotive, medical devices, promotional products, and toys. It is ideal for printing on products like circuit boards, syringes, pens, keychains, and other items with intricate or uneven surfaces.